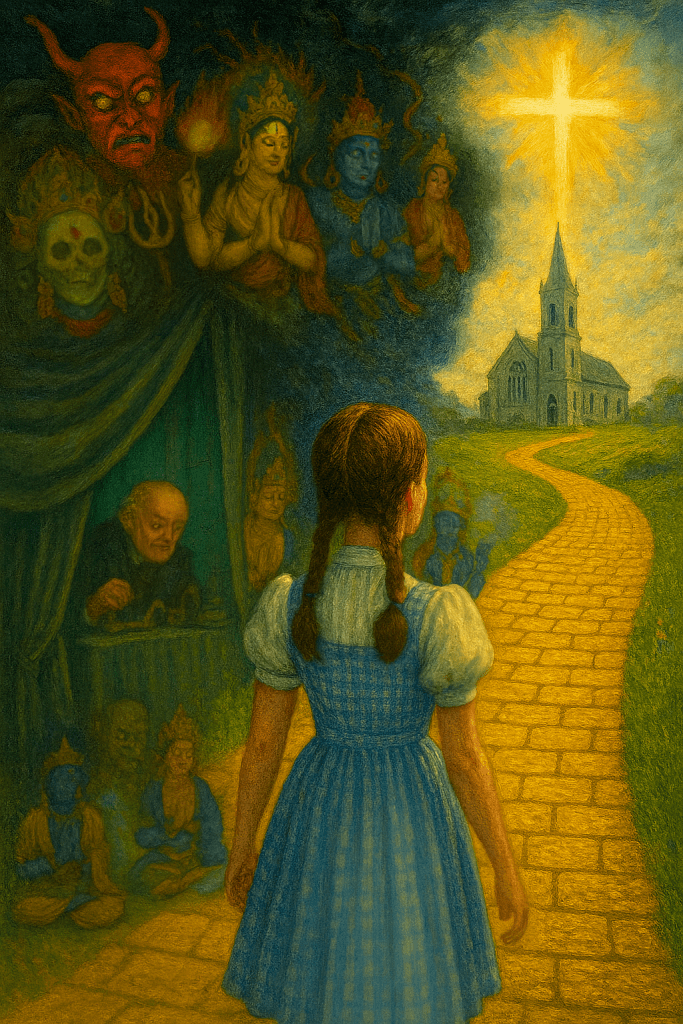There was once a man called Jeffrey Epstein.
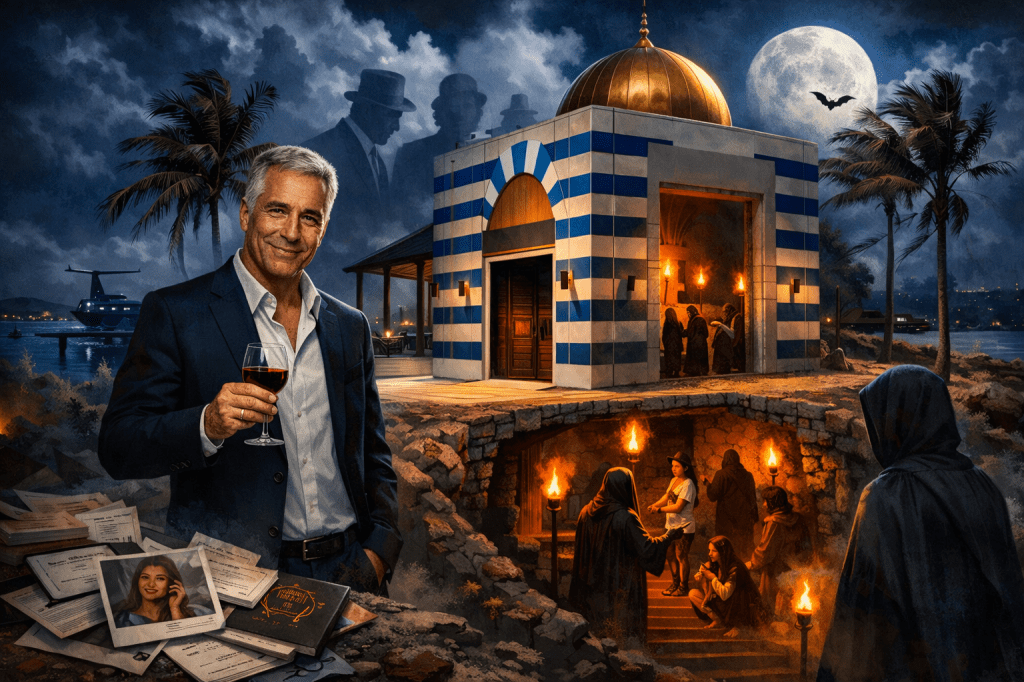
In public he was a benefactor of science, a patron of universities, and a familiar presence at elite gatherings where presidents, financiers, and scholars lifted glasses in his honor. He spoke often about innovation and the future of humanity. He funded research into artificial intelligence and longevity. He donated to museums and cultivated relationships with some of the wealthiest and most powerful people in the world.
In private, according to court findings and sworn testimony, he engaged in the sexual exploitation of underage girls. For years he maintained elite access even after a 2008 conviction in Florida that resulted in a widely criticized plea deal and a remarkably lenient sentence that allowed him to leave his jail cell to work in his office by day. His re-arrest in 2019 on federal sex trafficking charges exposed how effectively wealth, influence, and reputation had insulated him from deeper scrutiny.
Epstein seemed to understand a brutal rule of power: visibility can function as protection. The more photographed he was beside institutions of prestige, the less imaginable his alleged private conduct became to those outside his inner circle.
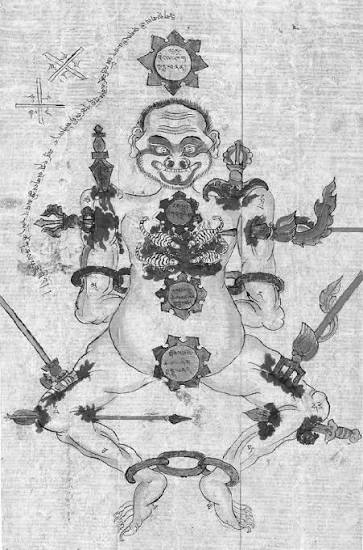
His gatherings were invitation-only, often held at his private island compound in the U.S. Virgin Islands. The architecture there blended minimalist modernism with a small blue-and-white striped domed structure that media outlets dubbed a “temple” because of its appearance. Guests described the environment as theatrical. Much of what occurred behind closed doors is documented only through depositions, allegations, and ongoing public debate.
Recently unsealed court documents, often referred to online as “the Epstein files,” have reignited public scrutiny. Thousands of pages of redacted emails including some visual material are being dissected not only by journalists but by ordinary citizens on TikTok, X, Reddit, and other platforms. Some social media users claim the documents reveal evidence of very extreme abuses beyond the charges formally brought in court, including references they interpret as ritualized harm or Satanic Ritual Abuse. These interpretations circulate widely online, though the verified criminal cases center on the exploitation and trafficking of minors.
Epstein was, by all outward appearances, a master of code-switching. By day he discussed finance, philanthropy, and global policy. By night, prosecutors allege, he participated in the exploitation of vulnerable girls. Private investigators with platforms on social media allege that he functioned as a sort of occult high priest who orchestrated acts of unimaginable depravity. He moved between these worlds without visible friction. Financier and social strategist in public; accused trafficker in private.
The deeper question is not merely how one man operated, but how systems of prestige allowed him to do so for so long. And whether others who participated in or enabled the abuse will ever face prosecution.
The Cult of Radiant Compassion
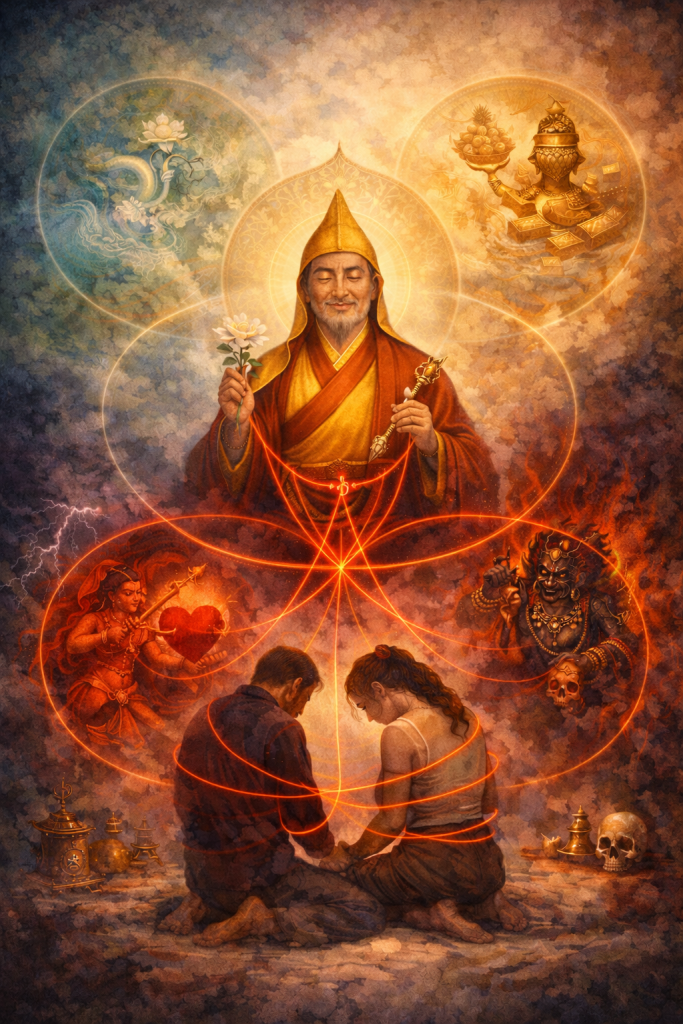
Across the ocean, in the mountains of distant lands, another structure flourished for centuries. Let’s just call it the Order of Radiant Compassion.
To outsiders, the Order appeared serene. Its temples were adorned with luminous murals depicting buddhas and bodhisattvas acting for the benefit of all sentient beings. Devotees spoke of nonviolence, transcendence of ego, and enlightenment.
But within the inner circles of the most accomplished adepts, a harsher doctrine was practiced. These gurus demanded absolute obedience. Students pledged sacred vows called samayas that many did not fully understand. Breaking those vows, they were warned, would condemn their consciousness to eons of unimaginable torment. Many vulnerable disciples were abused and gaslighted.
In this cult, the outer teachings emphasized kindness, while the secret teachings emphasized power and allowed for great cruelty. Advanced disciples were taught that reality could be manipulated through ritual and that consciousness could be fractured and reconstructed by tantric techniques. A disciple’s identity became malleable clay in the hands of the enlightened master who used those techniques to enforce his will. The language was luminous, but the implications were not.
Epstein’s circle believed themselves liberated from morality by intellect. The Order believed themselves liberated from morality by metaphysics. One cloaked itself in secular humanism, while the other cloaked itself in sanctified mysticism. Both relied on a similar architecture of control:
- Public virtue
- Private transgression
- Initiation through secrecy
- Loyalty secured by psychological or other forms of leverage
While some investigators have speculated that Epstein leveraged compromising information, the Order secured obedience through fear of karmic retribution and promises of enlightenment. In both systems, followers surrendered discernment in exchange for something greater.
The House of Mirrors
The lesson is not about one man’s island of horrors or one enlightenment cult flourishing through deception. It is about systems that divide the world into initiates and outsiders, that sanctify hierarchy, and that position certain people into positions of authority beyond moral scrutiny.
The public exposure of Epstein’s life shattered the illusion that prestige guarantees virtue. It forced a reckoning with how reputational power can silence victims for decades and how easily human beings are dazzled by proximity to influence. No system, whether financial, political, or spiritual, should ever place itself above ordinary morality. Accountability begins when we stop confusing the appearance of status with sanctity.