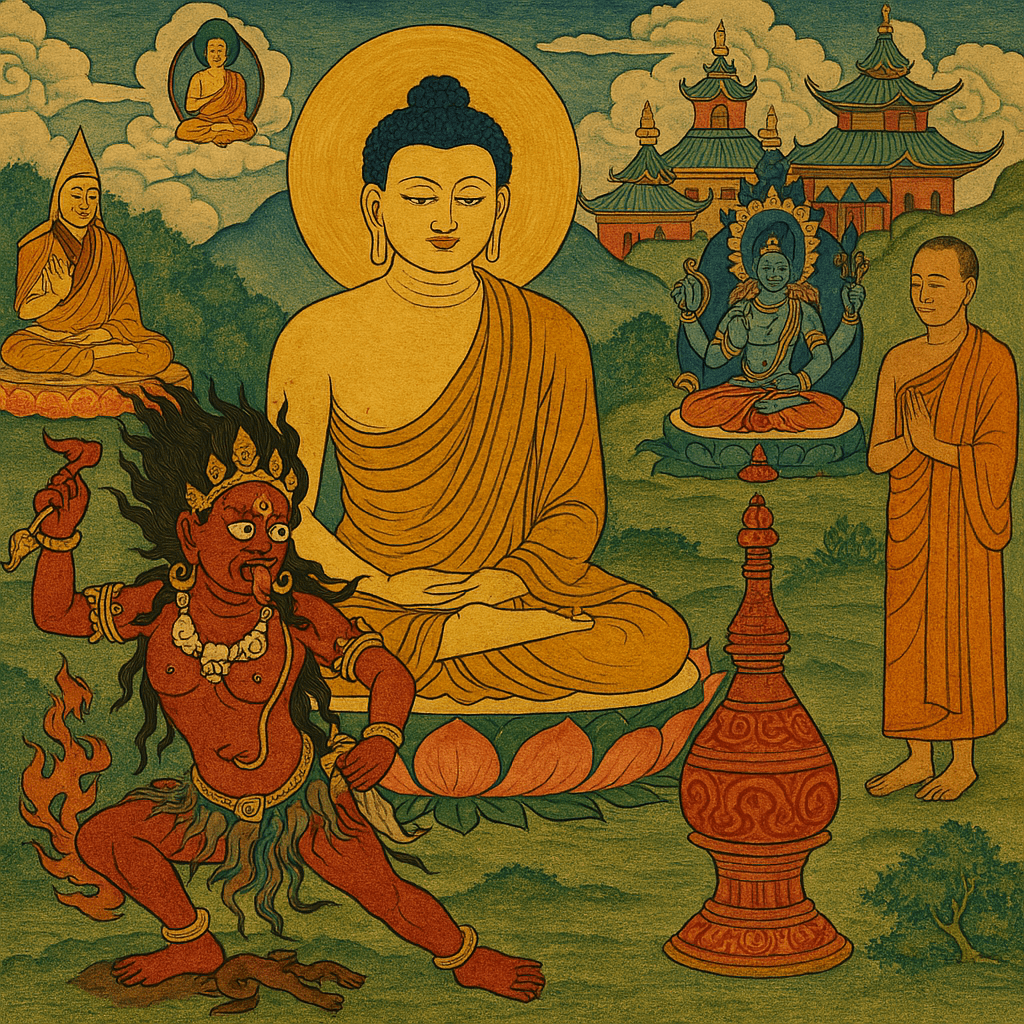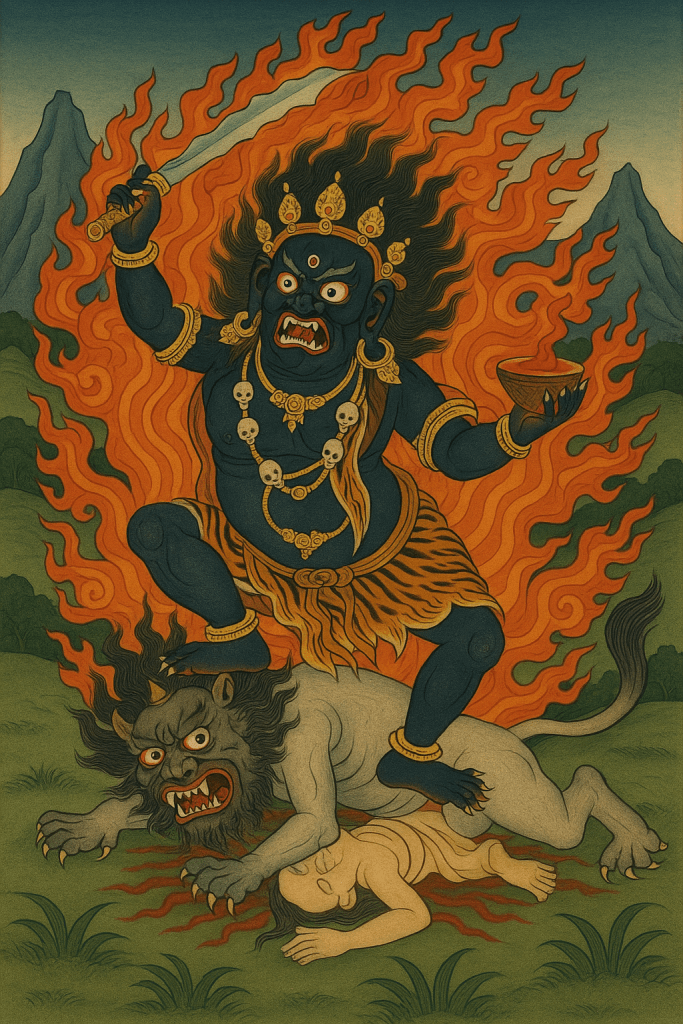
In this thangka-style painting, a wrathful tantric deity, likely Mahākāla, stands triumphant, engulfed in flames of spiritual power. He tramples a beast-like demon beneath his feet, which in turn crushes a human figure below. Far from mere symbolism, this hierarchy reveals a grim reality embedded in Tibetan tantric worldview: a cosmology where demons are organized in ranks, with wrathful deities occupying the highest tiers. These so-called “protector” spirits are themselves demonic in nature. They are powerful but subjugated through ritual, and are commanded by the guru to unleash violence against enemies of the dharma. The animal-like demon represents a lower-order spirit, weaponized by the deity. The crushed human symbolizes an actual person, someone the practitioner or lama has deemed a threat. The image is not just metaphor: it is a magical contract of domination.
Buddhists sometimes invoke ferocious protector deities like Mahākāla or Vajrakīlaya in rituals charged with violent imagery. In Tibetan history, such wrathful practices were often presented as spiritual rites to subdue obstacles, but evidence shows they could target actual enemies. For example, medieval Tibetan lamas served in warfare and politics: Lama Zhang (12th C. Kagyu) “engaged in political and military affairs” and even sent students into battle (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum), using tantric rituals and deities (like Vajravārāhī and Mahākāla) to subjugate foes. Under the Mongol Yuan, Tibetan Buddhist “magical warfare” became statecraft: Tsami Lotsāwa, a Tangut court chaplain, authored texts like “The Usurpation of Government,” a how-to on overthrowing rulers invoking Mahākāla against armies. When Genghis Khan’s siege faltered in 1210, Tibetan sources credit Mahākāla summoned by Tsami (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum) with bursting the Mongol siege dams and routing the attackers. The Mongols then adopted Mahākāla as their state protector. Likewise, Tibetan figures like the 8th Karmapa Karma Pakshi reportedly requested Mahākāla to exact revenge on his Chinese captors; lore even says Mahākāla “struck” the imperial palace (calling upon Mahakala…. | Ganachakra). Even the Nyingma saint Rwa Lotsāwa Dorje Drag (11th–12th C.) is celebrated in tradition for having “killed/murdered thirteen lamas” allegedly via Vajrabhairava rituals (Teacher: Rwa Lotsawa Dorje Drag). These and other incidents show tantric masters of Nyingma and Kagyu lineages historically appealed to protectors and demons in worldly struggles, not just inner battles.
Historical examples of tantric “war magic” include:
- Imperial warfare: Tibetan Buddhist shamans at the Tangut and Yuan courts summoned Mahākāla to combat invading armies (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum). Mongol ruler Qubilai Khan’s ritualist (the Sakya lama Dampa) was famed for invoking Mahākāla to turn back enemies; Mahākāla’s visage was later flown on Mongol battle banners (Himalayan Art: News) (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum).
- Sectarian conflicts: Rival Buddhist factions sometimes accused each other of violent tantra. (For example, later Gelugpa–Nyingma disputes mention rituals aimed at sectarian “enemies.”) In legend, a Kagyu master used Mahākāla to punish “impure” Gelugpas, and Dorje Shugden cult lore alleges victims of protector curses. (Such sectarian claims persist, though here we focus on pre-modern precedents.)
- Regional skirmishes: Kagyu and Nyingma yogins were known as healers and sorcerers. One Kagyu lama reportedly used protective rites to strike fear into rebels. Vajrabhairava, a wrathful Nyingma deity, was famously employed by Rwa Lotsāwa in ritual assassinations (one story credits him with killing Marpa Lotsāwa’s son, Dharma Dode) (Himalayan Art: News).
These accounts contradict the comforting piety that “the only enemies are our defilements.” Instead, Tibetan sources show tantric deities being literally invoked against human foes and armies. Even art and prayers reinforce this: Palden Lhamo, the Dalai Lamas’ protector, is often depicted brandishing a sword and holding a skull bowl “brimming with the blood of vanquished enemies” (Palden Lhamo: Supreme Guardian Goddess of the Dalai Lamas – Tibetan Buddhist Encyclopedia). Such imagery underscores that the deity’s “compassion” is militarized.
Violent Imagery in Ritual Texts
The ritual texts themselves are unapologetically graphic. For example, a common Vajrakīlaya (Krodha Phurba) sādhanā (prayer) reads like a battle spell. One verse proclaims that Vajrakīlaya wields weapons “with which even the whole great mountain Sumeru is crushed to dust,” and that he “grinds to atoms the nine Gong-po brothers of phenomenal existence” (Cult of the Deity Vajrakila). In context, the “Gong-po brothers” symbolize fundamental enemies or obstacles (often conceptualized as Mara’s forces or the mind’s afflictions), but the language is literal and violent.
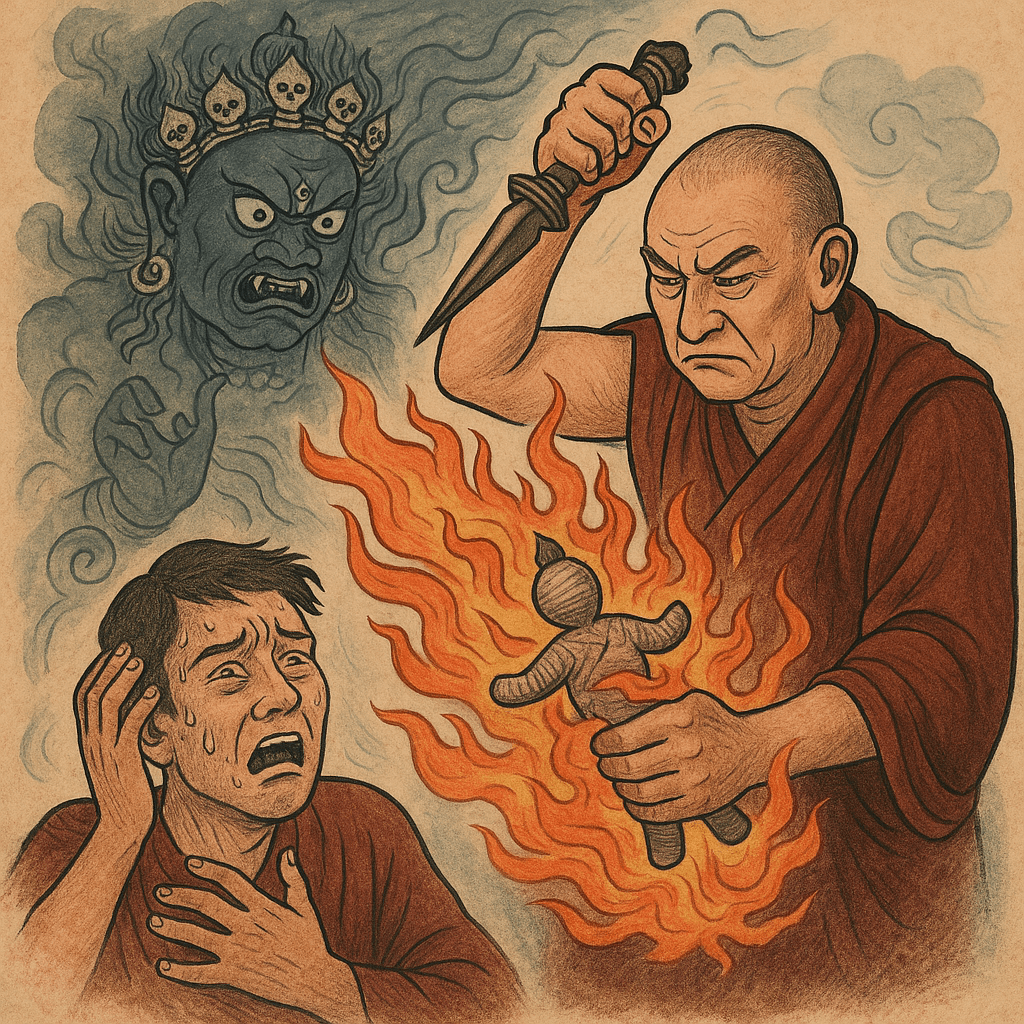
Texts on Mahākāla and Vajrabhairava likewise list long menus of violent exploits, trampling demons, cannibalizing spirits, or annihilating armies. In many kīlaya and bairaṇa (wrathful) rituals, the practitioner is explicitly instructed to cast forms or effigies of enemies into a bonfire or entangle them with magical ropes (Cult of the Deity Vajrakila) (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras). These are not purely abstract symbols but are described as actively destroying whoever or whatever they represent.
Indeed, scholar David Gray notes that Buddhist tantras use two kinds of violent rhetoric: grandiose, hyperbolic imagery to glorify the deity and impress the initiate, and actual ritual prescriptions for “violent ritual practices” (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras). While the former may seem merely figurative, Gray observes that even “symbolic” rituals often aim to harm the person symbolized (for example, burning an effigy of an enemy) (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras). Many tantra texts then justify these acts as transcending ordinary ethics: invoking a state of “non-dual gnosis” to excuse what would otherwise be murder (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras). In short, tantric sādhanās straddle symbolism and reality: they metaphorically crush delusions, but describe that metaphor in ultra-realistic, brutal terms accompanied by magical spells intended to harm human beings.
Empowered Lamas and “Transgressive” Rituals
Why this double talk? Tibetan lineages insist that only the most accomplished yogins (mahasiddhas) may perform such rites, precisely because they are “transgressive” and dangerous. The idea is that a realized master, having already tamed anger within, can safely wield wrath outside. As one modern analysis notes, advanced tantric practitioners are allowed “to invert Buddhist moral injunctions,” because rites aimed at killing are taught only to those senior enough to hold them (Buddhist Pacifists at War – JSTOR Daily). In practice, this meant kings, high lamas or court chaplains, not ordinary monks, performed these rituals.
Yet even senior masters often downplay the literal meaning today. Contemporary teachers frequently claim that prayers to “destroy enemies” really target the five poisons or ego-clinging, not people. (For instance, some explain Palden Lhamo’s blood bowl as symbolic of afflictions conquered.) Such interpretations align with inner-journey aspects of Vajrayāna. But history and ritual texts offer a different picture: these deities were invoked as warrior gods. Indeed, modern scholars argue that Buddhist tantra developed war-magic precisely because societies faced real threats. As Iain Sinclair puts it, defensive magic in early tantras was “pacifist in nature” but “destructive war magic also developed.” (Buddhist Pacifists at War – JSTOR Daily) Tantric manuals taught spells to freeze enemy armies with blizzards, sicken them with disease, or even consume them invisibly (Buddhist Pacifists at War – JSTOR Daily) ((PDF) War Magic: Religion, Sorcery, and Performance). One text in the Kālacakra cycle even provides a just-war framework, allowing only defensive conflict, infused with inner virtue, but this too presumes actual armed struggle (Buddhist Pacifists at War – JSTOR Daily).
This tension has sparked scholarly debate. Bryan Cuevas notes tantra’s fusion of “the internal and external worlds,” with protectors serving both spiritual and mundane power (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum). Gray emphasizes that, despite rhetoric, tantrics did prescribe lethal rituals, legitimized by claims to higher awareness (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras).
Critical Perspective and Conclusions
In light of this evidence, the standard assurance that wrathful protector practices are only symbolic ring hollow. Certainly, Vajrayāna doctrine can spiritualize violence, positing that a bodhisattva’s anger is “pure compassion.” But when lamas claim “I’m just crushing my own ego,” the historical record shows they were also legitimizing political or personal power plays. At the very least, the literalist language of the liturgies warrants skepticism. A practitioner chanting “grind my enemies into dust” is arguably invoking cosmic butchery, not just inner peace.
For modern readers, this does not necessarily indict all Vajrayāna practice for many make upstanding vows and use wrathful deities for healing or psychological aid. However, it does mean we should be wary of uncritical glosses. As Gray warns, tantra’s “ethical double standard,” appealing to transcendent insight to excuse violence, has been used to justify harmful actions even in contemporary settings (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras).
For those intrigued or unsettled by these findings, scholars continue to examine how Tibetan Buddhism navigates the gulf between its nonviolent ideals and its martial heritage. Controversies within the tradition and in academic circles reflect this struggle. What is certain is that any romantic notion of pacifist Buddhism must contend with the very real phenomenon of tantric war magic and the subjugation rituals conducted against human beings.
Further Reading: For critical scholarship on these issues, see Iain Sinclair’s “War Magic and Just War in Indian Tantric Buddhism” (Buddhist Pacifists at War – JSTOR Daily) (Buddhist Pacifists at War – JSTOR Daily) and Bryan Cuevas, “The Wizarding World of Tibetan Sorcery” (in Faith and Empire, esp. ch.5) (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum) (War Magic: Tibetan Sorcery | Rubin Museum). David B. Gray’s article “The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras” (2018) explicitly examines tantric prescriptions of violence (The Rhetoric of Violence in the Buddhist Tantras). Solomon FitzHerbert’s study of 17th-c. Tibetan “ritual propaganda” is also enlightening. (Online references: Rubin Museum’s “War Magic” exhibition, Himalayan Art archives, and academic discussions by Sinclair and Gray are excellent starting points.)