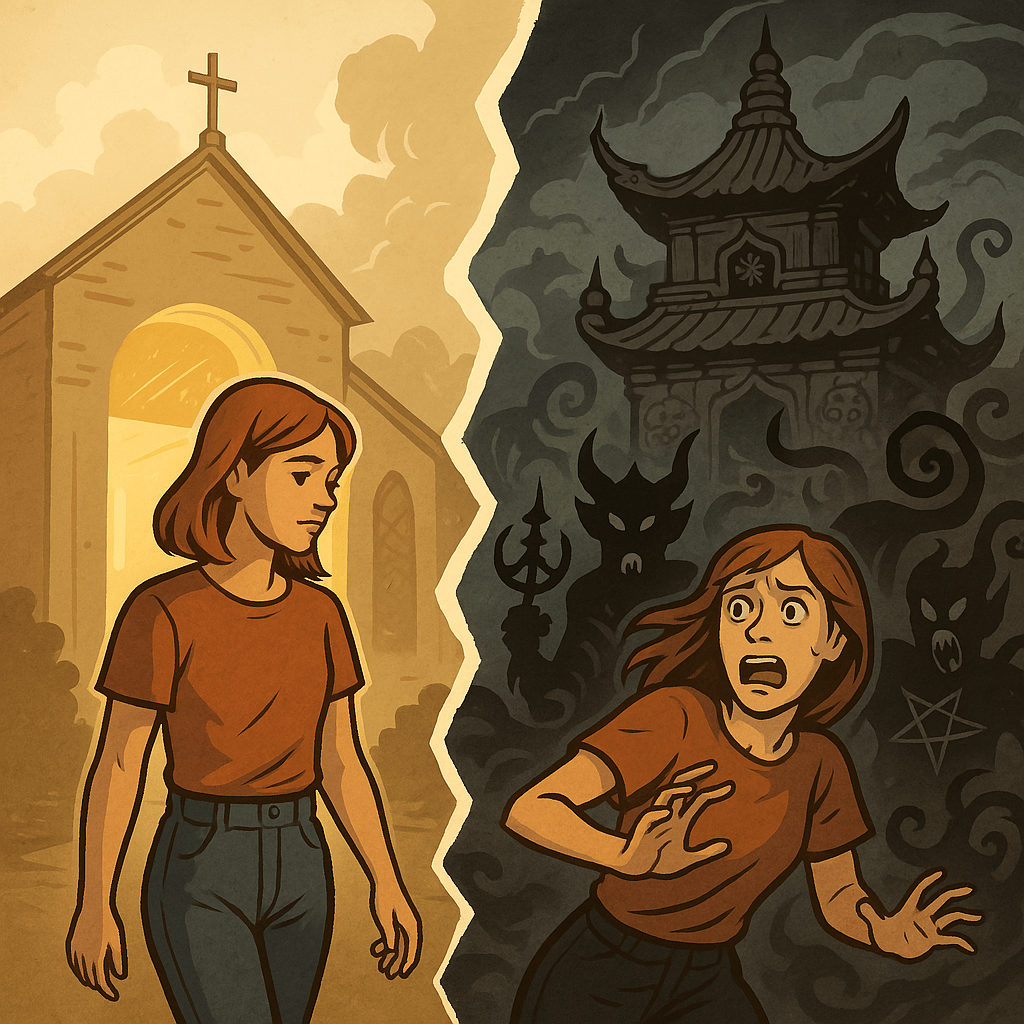
When I was fifteen, I walked away from the Catholic Church.
There was no drama, no spiritual backlash, no eerie sense of guilt or dread. I simply left. I had questions, and I didn’t know the answers. Like so many teenagers raised in religion, I drifted toward freedom, or what I thought was freedom. But I never stopped believing in Jesus Christ. I always knew He was real.
Still, for eight years, I lived outside the Church. No demons haunted me. No spiritual “agents” came after me. No dark force tried to pull me back or punish me. I was free to explore.
Then, at twenty-three, I was introduced to Tibetan Buddhism by a friend. Spiritual curiosity quickly became commitment. The teachings were deep, the rituals profound, and the promises huge. My belief in Jesus wasn’t challenged outright; instead, the gurus cleverly and swiftly recast Him as a “bodhisattva,” one of many enlightened beings in a cosmic buffet of spiritual options. I was told He was admirable, but not unique. Just another wise, and probably enlightened teacher.
I didn’t realize then how that subtle shift had planted the seeds of spiritual confusion. Over time, the practices became more demanding and more secretive. Eventually questions weren’t welcomed. When I began to notice darker occult elements woven into the heart of the practice, I had troubling doubts. The tantric path spoke of vajra hell, an eternal punishment for those who questioned or broke samaya (spiritual vows to the guru). And not just for betrayal or disobedience, but even for internal doubts.
And when I had them, everything changed.
I was tossed out. Not just socially or emotionally, but spiritually. I was attacked, not just by my former gurus, but by unseen forces. It was violent and supernatural. The very same tradition that had claimed to offer peace and enlightenment unleashed something very dark the moment I started to turn away from the guru.
This wasn’t like walking away from the Catholic Church. It was completely different. I experienced a spiritual assault of such magnitude that no one could believe me. And it begged the question: What kind of spiritual path tortures you for eternity for having doubts?
A demonic path does.The historical Buddha taught to question everything, but tantra did not allow it.
Tibetan Buddhism may parade as a tradition of compassion and peace, but my experience showed otherwise. If it were truly of the Light, it wouldn’t need to threaten vajra hell or unleash invisible tormentors on those who simply ask blunt and honest questions. It wouldn’t need to cloak the guru in infallibility while turning a blind eye to his abuse. And it certainly wouldn’t need to demonically retaliate against a soul simply for having doubts and trauma. The difference between the two paths couldn’t be clearer. When I left the Church, there was silence. When I left Tibetan Buddhism, there was war.