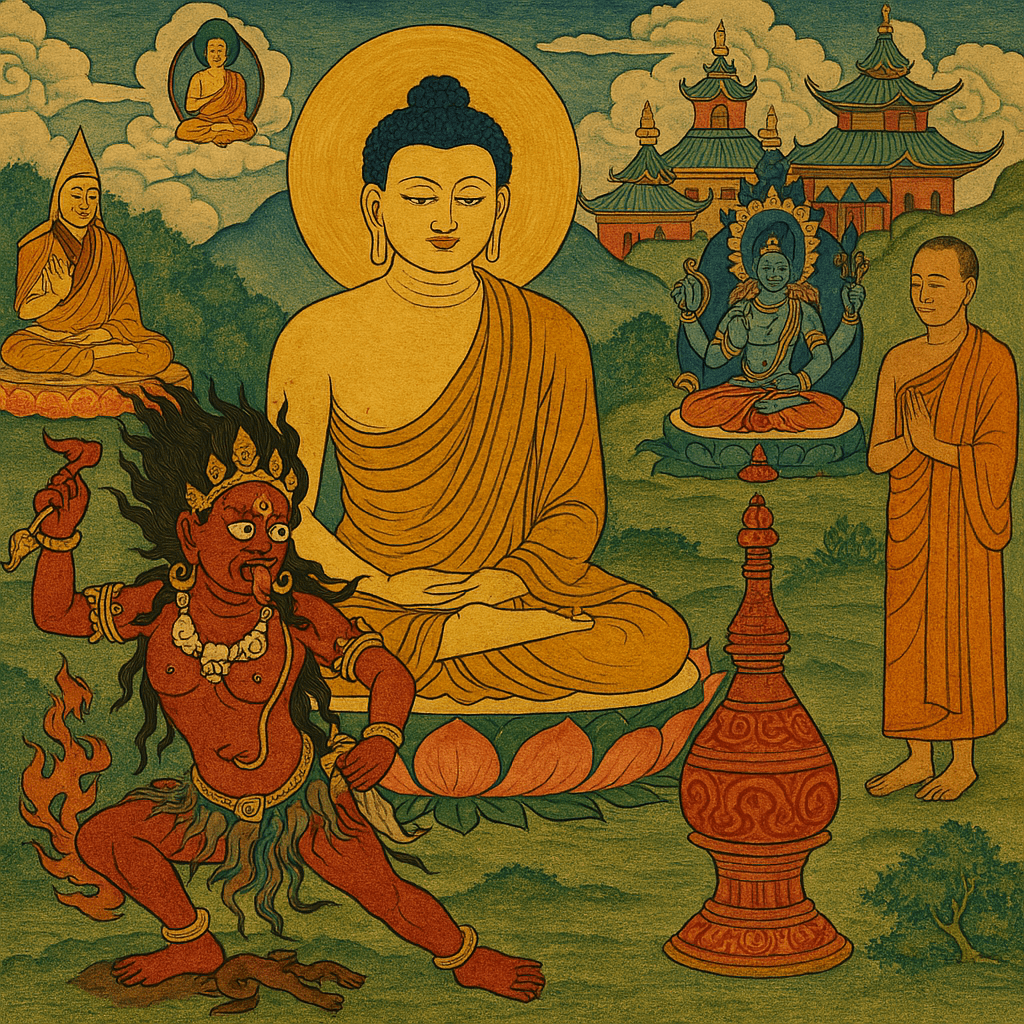
In both Hindu and Buddhist tantric traditions, Kali and Vajrayoginī stand as iconic figures of immense power. Wrathful, seductive, and liberating, they are revered as goddesses who destroy ignorance and ego, leading practitioners to freedom through terrifying grace. They drink blood, wear garlands of skulls, and dance on corpses. These are not symbols for the faint of heart.
Kali, in Hinduism, is the goddess of time and death. She is the dark mother who slays demons, severs illusion, and devours ego. Vajrayoginī, in Vajrayāna Buddhism, is a female buddha who leads devotees to enlightenment through the annihilation of dualistic perception, often through erotic and wrathful means.
Today, many feminists embrace these goddesses as symbols of female empowerment, strength, and liberation from patriarchal religion. But this overlooks the possibility that these figures, far from celebrating womanhood, may actually represent a deep spiritual hostility toward it. The ego-annihilation they demand may not be empowering at all, but destructive, both spiritually and psychologically. When viewed through a biblical lens, one must consider whether these so-called icons of empowerment are in fact hostile agents cloaked in feminine form. From a biblical worldview, who are they really?
Fallen Beings or Demonic Entities
If we take the Bible as the sole and literal authority:
- There is one true God (YHWH), and worship is due to Him alone.
- Any supernatural beings outside of YHWH and His angels fall under:
- Idols (Psalm 96:5 – “For all the gods of the nations are idols”)
- Deceiving spirits or demons (1 Corinthians 10:20 – “The sacrifices of pagans are offered to demons, not to God.”)
From this view:
| Deity | Biblical Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Kali | A manifestation of a demonic spirit that seduces worshippers through fear and false power |
| Vajrayoginī | A spirit of deception using mystical allure to imitate divine enlightenment |
Why They’re Considered Dangerous
1. They Accept Worship Not Meant for Them
- Worship of any being other than the God of Israel is strictly forbidden. (Exodus 20:3 – “You shall have no other gods before Me.”)
- Revering supernatural powers outside of God constitutes rebellion and idolatry.
2. They Promote False Teachings
3. They Offer Counterfeit Spiritual Power
- These goddesses can induce real mystical experiences through the occult third eye, but from a biblical view, such power is not from God.
- They mimic light and transcendence, offering access to preternatural realms that ensnare souls in spiritual bondage.
Biblical Warnings Relevant to These Figures
- 2 Corinthians 11:14 – “Even Satan disguises himself as an angel of light.”
- Deuteronomy 13:1–3 – Even if a sign or wonder comes to pass, if it leads you to follow other gods, it is a test from the Lord.
- Revelation 9:20 – Condemns worship of “idols of gold and silver… which cannot see or hear or walk.”
Summary (from a Biblical Lens)
Kali and Vajrayoginī are not misunderstood archetypes or symbolic feminine faces of divine truth. From a biblical standpoint, they are false gods or fallen spirits who lure seekers through mysticism, ecstasy, and power into worship that ultimately defies the true and living God.
Their powers are spiritual deceptions, designed to mimic enlightenment while leading souls away from salvation and the truth of Jesus Christ.
To those recovering from tantric abuse or deception: the biblical path does not deny spiritual reality, it affirms that spiritual warfare is real, and that freedom is found in Christ alone, not through altered states, or the worship of seductive wrathful or peaceful goddesses, or any other small “g” god for that matter.
You shall have no other gods before Me.” — Exodus 20:3